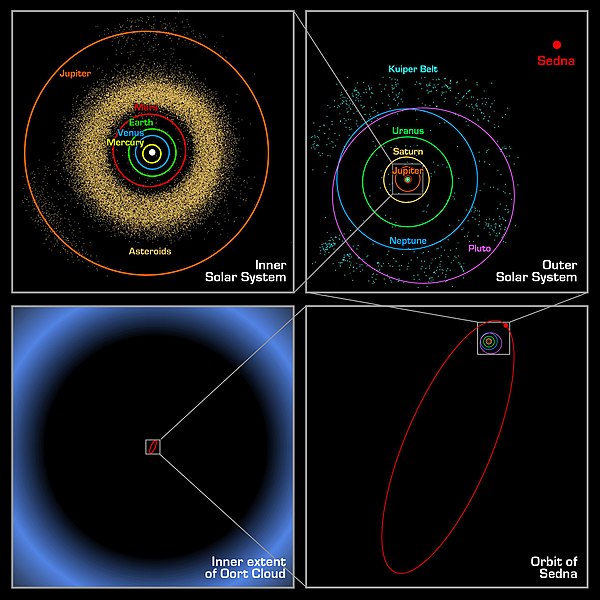
ფაილი:Oort cloud Sedna orbit.jpg
ზომა წინასწარი გადახედვისას: 600 × 600 პიქსელი. სხვა გაფართოება: 240 × 240 პიქსელი | 480 × 480 პიქსელი | 768 × 768 პიქსელი | 1 024 × 1 024 პიქსელი | 2 499 × 2 499 პიქსელი.
თავდაპირველი ფაილი ((2 499 × 2 499 პიქსელი, ფაილის ზომა: 542 კბ, MIME ტიპი: image/jpeg))
ფაილის ისტორია
დააწკაპუნეთ თარიღზე/დროზე ფაილის დასათვალიერებლად, როგორც ის მაშინ გამოიყურებოდა.
| თარიღი/დრო | მინიატიურა | ზომები | მომხმარებელი | შენიშვნა | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| მიმდინარე | 08:48, 19 სექტემბერი 2005 |  | 2 499×2 499 (542 კბ) | Bricktop | larger |
| 00:05, 24 მარტი 2005 |  | 577×577 (47 კბ) | Smartech~commonswiki | {{PD-USGov-NASA}} |
ბმულები
ეს ფაილი არცერთ გვერდზე არ გამოიყენება.
ფაილის გლობალური გამოყენება
ეს ფაილი გამოიყენება შემდეგ ვიკებში:
- გამოყენება ba.wikibooks.org-ში
- გამოყენება bg.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება bn.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება bn.wikibooks.org-ში
- გამოყენება cs.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება da.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება de.wikibooks.org-ში
- გამოყენება el.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება en.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება en.wikibooks.org-ში
- გამოყენება es.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება fi.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება fr.wikibooks.org-ში
- გამოყენება hu.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება id.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება is.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება it.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება kn.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება lt.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება mr.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება ms.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება mt.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება nds.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება nl.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება oc.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება pl.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება pms.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება pnb.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება sh.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება simple.wikipedia.org-ში
- გამოყენება sk.wikipedia.org-ში
იხილეთ, ამ ფაილის გლობალური გამოყენება.